Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Image cropping¶
By cropping unwanted outer areas can be removed from a CLSM image. The process usually consists of the removal of peripheral areas of an image to remove extraneous trash from the picture, to improve its framing, to change the aspect ratio. Cropping of CLSM images in tttrlib preserves the information contained in the associated photons, i.e., the micro time, the macro time, and the routing channel numbers.
from __future__ import print_function
import tttrlib
import numpy as np
import pylab as plt
Read data of the CLSM image and fill CLSM image with photon information.
data = tttrlib.TTTR('../../tttr-data/imaging/pq/ht3/crn_clv_img.ht3')
settings = {
"channels": [0, 1],
"fill": True,
}
image = tttrlib.CLSMImage(data, **settings)
The CLSM image of this example has 40 frames and 256x256 pixles.
image.shape == (40, 256, 256)
im = image.intensity.sum(axis=0)
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()
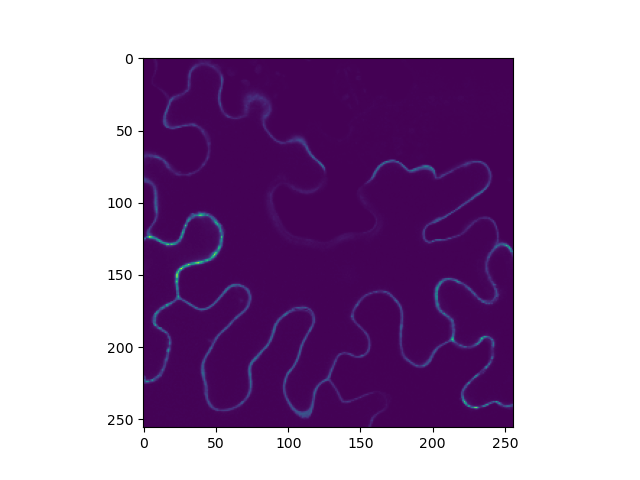
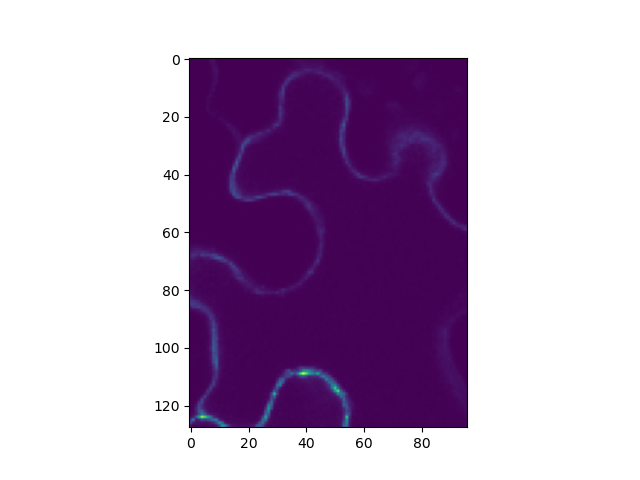
The CLSM image is cropped by providing the frame index bounds amoung the shape of the new CLSM image.
frame_start = 5
frame_stop = 20
image.crop(frame_start, frame_stop, 0, 128, 0, 96)
image.shape == (15, 128, 96)
im = image.intensity.sum(axis=0)
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.825 seconds)