Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Image transform¶
TTTR CLSM images are constructed of photons that are grouped into pixels. For each photon the micro time, the macro time and the registering detector is stored as additional information, w. A transformation is a function that maps one set to another set after performing some operations. An image transform is a function that maps one image to another image. Instead of operating on gray level intensity of and image at any point. Photons (including their additional information) are mapped to a new image. Such a mapping can eg for non-affine and affine transforamtions (rotations, streching, etc.). Below a very simple image transformation (scaling/streching) is illustrated.
Note: Transformations of CLSM images changes the temporal ordering of the photons. Hence, a transformed images cannot be used for advanced data analyis such as image correlation. Try to plan your experiment optimally and aquire the data as needed (pixel dwell times, laser power, etc.).
from __future__ import print_function
import tttrlib
import numpy as np
import pylab as plt
Read data of the CLSM image
data = tttrlib.TTTR('../../tttr-data/imaging/pq/ht3/crn_clv_img.ht3')
# Read contents of file into new CLSMImage
settings = {
"channels": [0, 1],
"fill": True,
}
image = tttrlib.CLSMImage(data, **settings)
img_original = image.intensity.sum(axis=0)
# Transform
# do a 4x4 binning
bin_line = 4
bin_pixel = 4
n_frames, n_lines, n_pixel = image.shape
n_px = n_frames * n_lines * n_pixel
# interleaved 1D array of origin and target indices.
mapping = np.empty(n_px * 2, dtype=np.uint32)
i = 0
for f in range(0, n_frames):
for l in range(0, n_lines):
for p in range(0, n_pixel):
source_idx = image.to1D(f, l, p)
# In this example the lines and pixels are binned by a factor of 4
target_idx = image.to1D(f, l // bin_line, p // bin_pixel)
mapping[i + 0] = source_idx
mapping[i + 1] = target_idx
i += 2
# Any other arbitrary mapping cloud be used
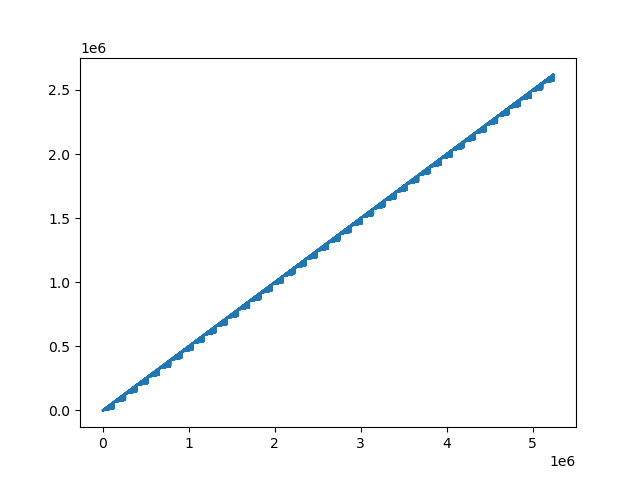
plt.plot(mapping)
plt.show()
image.transform(mapping)
img_transformed = image.intensity.sum(axis=0)
# Plot the results
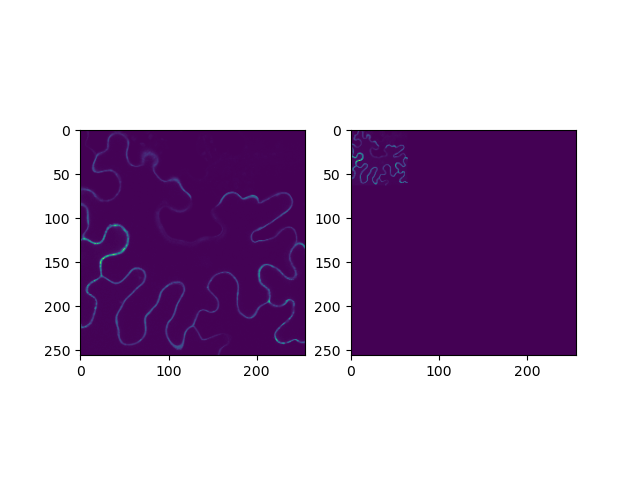
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2)
axs[0].imshow(img_original)
axs[1].imshow(img_transformed)
plt.show()
# After transforming the image can be cropped
image.crop(0, n_frames, 0, n_lines // bin_line, 0, n_pixel // bin_pixel)
img_transformed_cropped = image.intensity.sum(axis=0)
# Plot the results
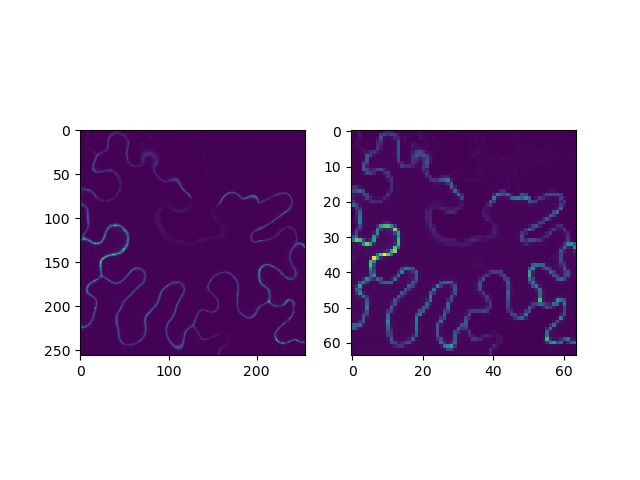
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2)
axs[0].imshow(img_original)
axs[1].imshow(img_transformed_cropped)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 7.045 seconds)