Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Convolution routines¶
Overview¶
In tttrlib there are a set of different convolution routines that can be used to compute
fluorescence decays. Most fluorescence decays are linear combinations of exponential
decays. Convolutions of such fluorescence decays with instrument response functions
can be computed using the routines (fconv, fconv_per, fconv_per_cs, etc.). Here,
fconv stands for fast convolution.
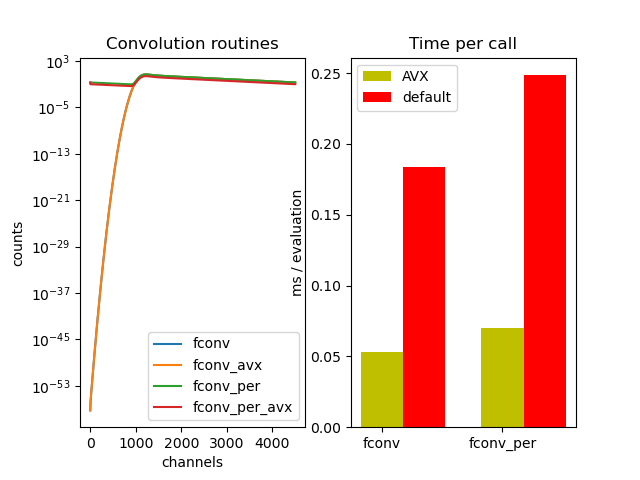
For faster convolutions tttrlib provides routines that make use of
SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data). The SIMD routines use of the AVX2 extension
(Advanced Vector Extension). For instance, the routines fconv and fconv_per
(periodic convolution) have corresponding SIMD routines named fconv_avx``and
``fconv_per_avx. The SIMD routines compute in parallel the decay in cases
the decay is compose of more than a single fluorescence lifetime.
The SIMD AVX make use of AVX2 and FMA (Fused Multiply Add). AVX2 and FMA require CPUs with ‘modern’ instruction sets. Most x86 CPUs that were manufacture since 2012 are supported.
from __future__ import annotations
import tttrlib
import scipy.stats
import time
import numpy as np
import pylab as p
Illustrate the different convolution methods for a computed instrument response function (IRF). Excitation period, i.e., the time between two subsequent excitation pulses Number of micro time channels (usually, linear spacing of micro time channels)
period = 16
n_channels = 4505
irf_position = 4.0
irf_width = 0.25
time_axis = np.linspace(0, period, n_channels)
irf = scipy.stats.norm.pdf(time_axis, loc=irf_position, scale=irf_width)
dt = time_axis[1]-time_axis[0]
lifetime_spectrum = np.array([1., 4, 1., 0.4] * 4)
model = np.zeros_like(irf)
stop = len(irf)
start = 0
Convolution method |
function name |
|---|---|
Fast convolution |
fconv |
Fast periodic convolution |
fconv_per |
Fast convolution (AVX) |
fconv_avx |
Fast periodic convolution (AVX) |
fconv_per_avx |
Fast periodic convolution (with stop) |
fconv_per_cs |
Fast convolution with reference compound |
fconv_ref |
Convolution of decay curve and IRF |
sconv |
n_runs = 50
times = list()
times_avx = list()
names = ["fconv", "fconv_per"]
t_start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(n_runs):
tttrlib.fconv(fit=model, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ex = time.perf_counter() - t_start
times.append(ex)
t_start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(n_runs):
tttrlib.fconv_avx(fit=model, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ex = time.perf_counter() - t_start
times_avx.append(ex)
t_start = time.perf_counter() # in seconds
for _ in range(n_runs):
tttrlib.fconv_per(fit=model, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, period=period, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ex = time.perf_counter() - t_start
times.append(ex)
t_start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(n_runs):
tttrlib.fconv_per_avx(fit=model, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, period=period, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ex = time.perf_counter() - t_start
times_avx.append(ex)
times = np.array(times) * 1000.0 / n_runs
times_avx = np.array(times_avx) * 1000.0 / n_runs
# make plots
##################
fig, ax = p.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, sharex=False)
ax[0].set_title('Convolution routines')
ax[0].set_ylabel('counts')
ax[0].set_xlabel('channels')
model = np.zeros_like(irf)
tttrlib.fconv(fit=model, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ax[0].semilogy(model, label="fconv")
model_avx = np.zeros_like(irf)
tttrlib.fconv_avx(fit=model_avx, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ax[0].semilogy(model, label="fconv_avx")
model = np.zeros_like(irf)
tttrlib.fconv_per(fit=model, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, period=period, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ax[0].semilogy(model, label="fconv_per")
model = np.zeros_like(irf)
tttrlib.fconv_per_avx(fit=model, irf=irf, x=lifetime_spectrum, period=period, start=start, stop=stop, dt=dt)
ax[0].semilogy(model, label="fconv_per_avx")
ax[0].legend()
# Benchmark
ax[1].set_title('Benchmark')
ax[1].set_ylabel('ms / evaluation')
ind = np.arange(len(times)) # the x locations for the groups
ax[1].set_title('Time per call')
ax[1].set_xticks(ind)
ax[1].set_xticklabels(names)
width = 0.35
ax[1].bar(ind, times_avx, width, color='y', label='AVX')
ax[1].bar(ind + width, times, width, color='r', label='default')
ax[1].legend()
p.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.304 seconds)